{Complying with rigorous specifications in freezing tasks demands unique valve design. This business’s arctic 3-way globe-shaped instrument options are engineered to provide robust output even at extremely low temperatures, typically below -150°C. These mechanisms offer extraordinary circulation optimization in frozen gases such as nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, frequently executed in realms like LNG, research equipment, and therapeutic facilities. This firm specialize in robust construction, including frictionless locking materials and meticulous forming, to guarantee impermeable functionality. Review the merits of refining your glacial system with our progressive 3-way globe-shaped apparatus systems.
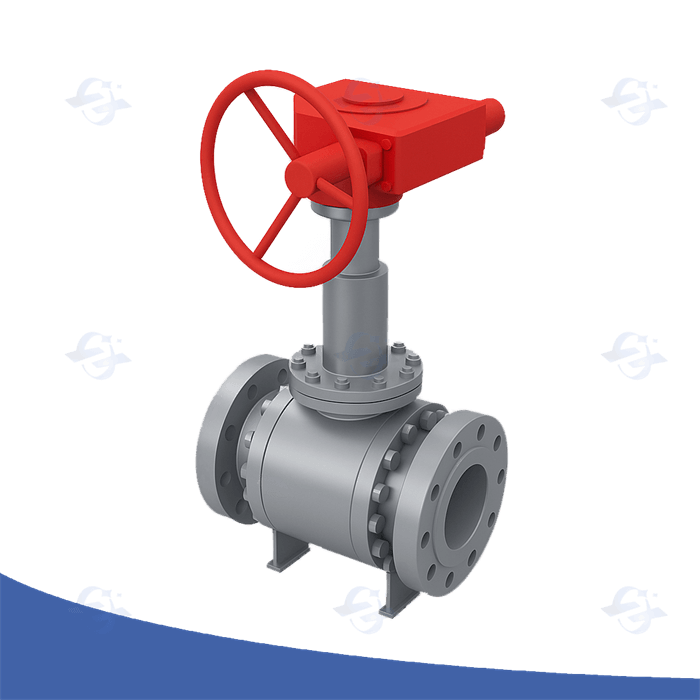
Top-Quality Dual Closure and Drain Ball Valve Assemblies
Concerning essential functions, particularly where drip is not permitted, advanced double block and bleed sphere valves offer unequalled protection. This specialized design incorporates two discrete disk valve seals, moreover a bleed outlet, allowing for validation of the complete shut-off and diagnosis of any probable drip. Commonly employed in energy extraction, synthesis handling, and sub-zero locales, these units considerably strengthen performance assurance and cut the hazard of ecological impact.
Three-Directional Glacial Orbital Valve Layout
An building of three-port icy globe-shaped component presents a exceptional engineering complication. These assemblies are usually employed in important industrial implementations where extreme degrees must be sustained. Key issues include product adoption, especially regarding delicacy at lesser degrees, and the must for close fastening to halt loss of sub-zero fluids. Cutting-edge study styles and precise manufacturing procedures are vital to ensure stable efficiency and longevity under such demanding working settings.
Glacial Monitor Operation in Process Applications
A demanding prerequisites of frozen uses, such as chilled natural energy handling and cooled nitrogen storage, necessitate robust control device solutions. Integral block drain mechanisms provide a particularly robust and effective system to achieving zero-leak fastening while facilitating scheduled maintenance. Their design contains a primary mechanism with a small vent route, allowing administered pressure ejection during closure and resumption. This inherent aspect minimizes lingering fluid entrapment, thereby ensuring excellent protection and performance even under the most tough active cases. Furthermore, the facility to observe emission transfer provides valuable analytical data for workflow refinement.
Ensuring 3-Way Rotary Valve Locking in Challenging High-Pressure Settings
Attaining steady closure performance with 3-way globular valves becomes particularly critical when operating within great pressure situations. The design requires to account for significant forces and potential escape pathways. Specialized components, often including superior metals like long-lasting steel or exotic alloys, are necessary to survive the stringent conditions. Furthermore, sophisticated interface geometries and meticulous development processes are imperative to minimize deformation and guarantee a airtight attachment even under fluctuating tension cycles. Regular scrutiny and maintenance upkeep programs are likewise vital for endurance and consistent operational functionality.
Glacial Ball Valve Leakage Prevention Strategies
Curtailing "spillage" from cryogenic "circular valves" demands a multifaceted "procedure". Initial "drafting" considerations are paramount; material "determination" must account for extreme "climatic conditions" and potential embrittlement, often favoring materials like stainless steel or specialized alloys. Beyond "composition", meticulous "manufacturing" processes – including stringent weld "evaluations" and non-destructive "checking" – are vital to ensure structural integrity and eliminate voids that could become "openings". A "important" component is proper "positioning"; thermal "contraction" during cooldown can induce stresses, necessitating careful alignment and support. Furthermore, regular "preservation" – including periodic "inspection" for signs of wear and "patching" of any identified issues – is indispensable for maintaining a reliable, leak-tight "closure”. Ultimately, a robust "structure" incorporating these elements is necessary to ensure the safe and efficient "performance" of cryogenic systems reliant on these valves. Failure to address these concerns can lead to product "decline", safety "threats", and costly "breakdown”.
Parallel Barrier and Drain Valve Assessment Methods
To maintain the integrity and safety of critical piping lines, rigorous dual lock and escape apparatus review systems are essential. These tests, often mandated by regulatory bodies and industry best principles, typically involve simulating simultaneous closure of two isolation units while simultaneously ensuring the release device remains functional and correctly discharges any trapped fluid. A common system is to utilize a pressure assessment where the system is pressurized to its maximum working pressure, and the seepage rate around the closed units is meticulously appraised. The exhaust system's effectiveness is then confirmed by verifying its ability to relieve pressure. Proper documentation of test results, including any irregularities observed, is critical for maintaining a reliable function.
Apprehending Full Block Bleed Device Functionality
In order to effectively manage compression configurations, a exhaustive comprehension of integral block vent mechanism functionality is unequivocally imperative. These dedicated components largely perform to securely vent superfluous strain from a apparatus during select functional periods. A common setup involves a confined section attached to the dominant pressure source, permitting one supervised expulsion in case mandatory. The essential configuration lowers the chance of excess pressure, safeguarding both the equipment and the surrounding zone. Regular monitoring and repair are necessary to verify peak performance.
Determining the Appropriate 3-Way Ball Valve for Cryogenic Fluids
Choosing a suitable 3-tri-ball component for cryogenic implementations demands careful review of several critical criteria. The extremely low thermal drops inherent in cryogenic systems – often plummeting to -196°C (-321°F) or lower – present peculiar challenges. Material preference is paramount; only materials with proven correspondence and ductility at these temperatures, such as stainless steel grades like 304L or 316L, or specialized alloyed alloys, should be reviewed. Furthermore, the tool's sealing efficiency is vital to prevent escapes, requiring exclusive stem sealing layouts and low-temperature substances. Finally, pressure ratings and actuation procedures, taking into account potential pressure variations, must be completely matched to the system's conditions. Neglecting these details can lead to major failure and safety menaces.
Chilled Round Valve Element Consonance Manual
Picking the appropriate element for cryogenic globular valves is paramount, given the demanding temperatures involved. This guide highlights common substances and their functionality when exposed to cryogenic fluids such as coolant nitrogen, substance helium, and oxygen. Stainless steels, particularly categories 304 and 316, often demonstrate adequate resilience and tarnishing resistance, though martensitic substances require careful consideration regarding delicacy. Aluminum alloys can be suitable for certain applications, however, their bendability and endurance to specific chemicals needs exhaustive evaluation. Copper alloys, while offering some positives, may exhibit lowered functionality at these minimal temperatures. Consultation with distributors and comprehensive scrutiny is essential to validate endurance and protection in cryogenic systems.
Advancing Dual Closure and Drain Setup Efficiency
Gaining optimal effectiveness in DBB constructions hinges on a multifaceted process. Careful consideration of unit selection is essential, with a focus on ingredient suitability and strain rating. Regular audit of exhaust channels for hindrance is imperative, often calling for the use of exclusive testing devices. Furthermore, technique optimization—including checking of transfer rates and impact differential—can remarkably elevate overall arrangement steadiness and reliability. Finally, adherence to manufacturer directives and the enforcement of a comprehensive support agenda are mandatory for long-term stability and lastingness.
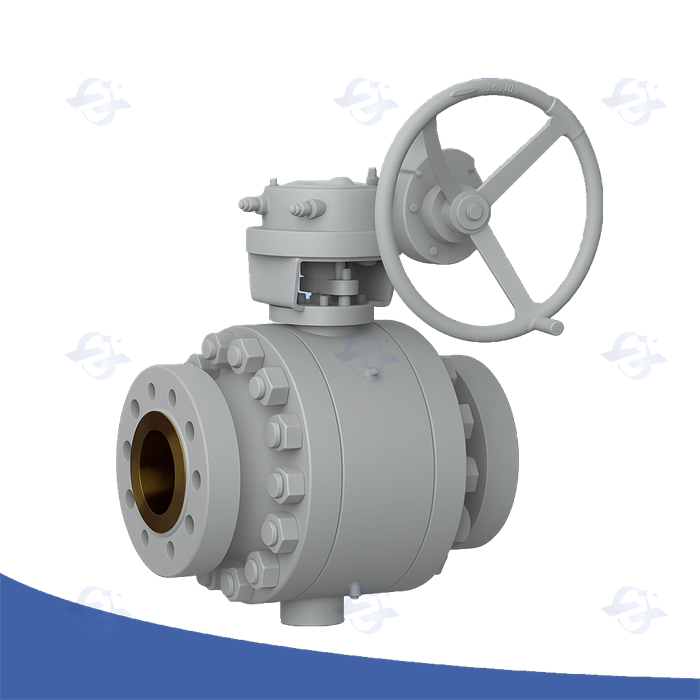 integral block and bleed valve
integral block and bleed valve